
Directive on Administrative Cooperation (DAC 6)
New EU tax Mandatory Disclosure Rules (MDR)

|
Update: 1 January 2021 Read our insights for further details 'Implications of the Free Trade Agreement with the EU for DAC 6'. |
Tackling tax avoidance and evasion is a key part of the UK government’s strategy to ensure that everyone pays their fair share of tax.
The UK has worked closely with the OECD, the EU Commission and other EU member states to introduce the Directive on Administrative Cooperation (DAC) in 2011 to find ways to effectively identify and tackle these kinds of arrangements.
The latest amendment to the DAC is commonly known as DAC 6, which was effective on 25 June 2018. Member states were in principle required to put in place legislation giving effect to the provisions of the Directive by 31 December 2019.
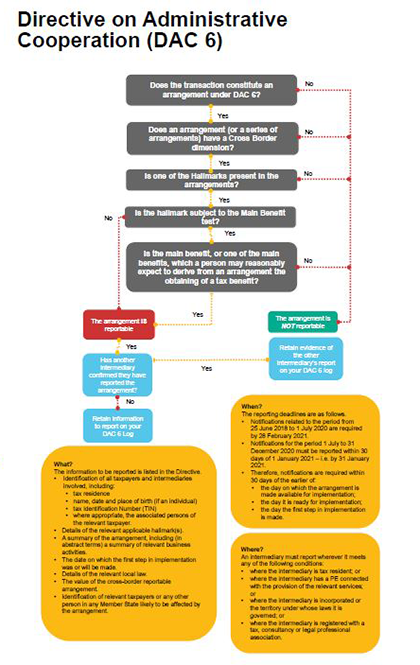
What is DAC 6?
DAC 6 imposes mandatory reporting of reportable arrangements which:
- are cross-border affecting at least one EU Member State or the UK and which
- fall within one of a number of 'hallmarks'.
The hallmarks are characteristics commonly seen in arrangements which could be used to avoid or evade tax but as drafted, they can also catch many commercial arrangements.
From a UK perspective, DAC 6 covers all EU taxes other than VAT, customs duties, excise duties and mandatory social security contributions.
The legislation sets out who has to report, what arrangements have to be reported, the deadlines for reporting, and what information needs to be reported.
Who has to make the report?
The reporting obligations fall on 'intermediaries' or, in some circumstances, the taxpayer itself.
Intermediaries who advise on cross-border transactions need to prepare so they can make any required report on time.
Who does it apply to?
DAC6 applies to any person (including an individual, partnership, company or other legal entity) operating in the EU or with interests in the EU. So it could apply to multinational companies. It also applies to intermediaries such as law firms, accountants, banks and financial advisors.
DAC 6 is primarily aimed at intermediaries. However there are some circumstances where a taxpayer may have to make a report. If you are a taxpayer, this guide for taxpayers sets out some more information about 'Getting ready for DAC 6'.
Do I need to report under DAC 6?HMRC issued the Regulations in January 2020 and the legislation came into force on 1 July 2020. HMRC published their guidance on the same date which is here. This means that DAC 6 will still apply to the UK even though is not a member of the EU following Brexit. (However as matters stand at the time of writing, once the transition period ends on 31 December 2020 the requirement to make future reports will be limited to cross-border arrangements that involve the EU member states). In order to assess whether a report may need to be made, any arrangements should be assessed against the following questions:
When is the report deadline?Due to COVID-19, the reporting deadlines were extended with the first notifications required by 30 January 2021 for the period from 1 July to 31 December 2020 and by 28 February 2021 for the period before 1 July 2020 (when the rules come into effect). These must include reporting arrangements where the first step of the arrangement was made after 25 June 2018 (when the directive came into force) and before 1 July 2020. |
|
The implementation of the extension means:
- Historical reporting covering arrangements in the period from 25 June 2018 to 30 June 2020 will be postponed from 31 August to 28 February 2021.
- The reporting obligations arising from 1 July to 31 December 2020 are now deferred to 1 January 2021. Such reports are required within 30 days beginning with that date. As the reporting dates fall on a weekend, it may be prudent to submit the reports by close of business on Friday 29th January 2021. Although based on HMRC usual practice, we would expect them to accept reports by first thing on Monday 1 February 2021 as being on time.
- Information will not be exchanged between Member States until 30 April 2021.
Thereafter (excluding cases involving legal professional privilege), reports (for both intermediaries and taxpayers) will need to be filed within 30 days of the earlier of the day on which the arrangement is made available for implementation, the day it is ready for implementation, and the day the first step in implementation is made.
There are ongoing quarterly reporting obligations for 'marketed arrangements' – marketed tax schemes which can be implemented with minimal customisation.
Non-compliance by either intermediaries or taxpayers will attract penalties. These can be broadly up to £5,000 or a daily penalty of £600 for continuing failure.
What should be reported?
The information to be reported is listed in the Directive:
- Identification of all taxpayers and intermediaries involved, including:
- tax residence
- name, date and place of birth (if an individual)
- Tax Identification Number (TIN).
- where appropriate, the associated persons of the relevant taxpayer
- details of the relevant applicable hallmark(s)
- a summary of the arrangement, including (in abstract terms) a summary of relevant business activities
- the date on which the first step in implementation was or will be made
- details of the relevant local law
- the value of the cross-border reportable arrangement
- identification of relevant taxpayers or any other person in any Member State likely to be affected by the arrangement.
Whichever intermediary/taxpayer is making the report will clearly need to devote time to collating information, but will also need to ensure others involved are lined up to cooperate with this process. Even if you are not the intermediary responsible for making the report, you will need to retain confirmation that another intermediary is making the report.
How to make a report
HMRC have confirmed that they intend for taxpayers to make reports under DAC 6 via a portal. The portal is currently in development and is expected to be available before the first reporting deadline.
If you need any further assistance regarding DAC 6, please contact Jane Mackay, Head of Tax.
Table 1: The Definitions
Table 2: The Hallmarks
Categories |
Hallmarks |
Main Benefit Test |
|
Category A
|
Taxpayer or participant under a confidentiality condition in respect of how the arrangements secure a tax advantage. Intermediary paid by reference to the amount of tax saved or whether the scheme is effective. Standardised documentation and/or structure which is available to more than one taxpayer. |
|
|
Category B |
Loss-buying. Converting income into capital. Circular transactions resulting in the round-tripping of funds with no other primary commercial function. |
|
|
Category C
|
Deductible cross-border payment between associated persons.
Deductions for depreciation claimed in more than one jurisdiction. Double tax relief claimed in more than one jurisdiction in respect of the same income. Asset transfer where amount treated as payable is materially different between jurisdictions. |
|
|
Category D |
Arrangements which have the effect of undermining reporting requirements under agreements for the automatic exchange of information. |
|
|
Category E |
Arrangements involving the use of unilateral transfer pricing safe harbour rules. Transfers of hard to value intangibles for which no reliable comparables exist where financial projections or assumptions used in valuation are highly uncertain. Cross-border transfer of functions/risks/assets causing a more than 50% decrease in earnings before interest and tax during the next three years. |
Contact us
