Tax Season Speedway 2025: Investors
1. Tax rates are significantly more favourable for dividend income than interest income. The top personal tax rates in Ontario for 2025 are as follows:
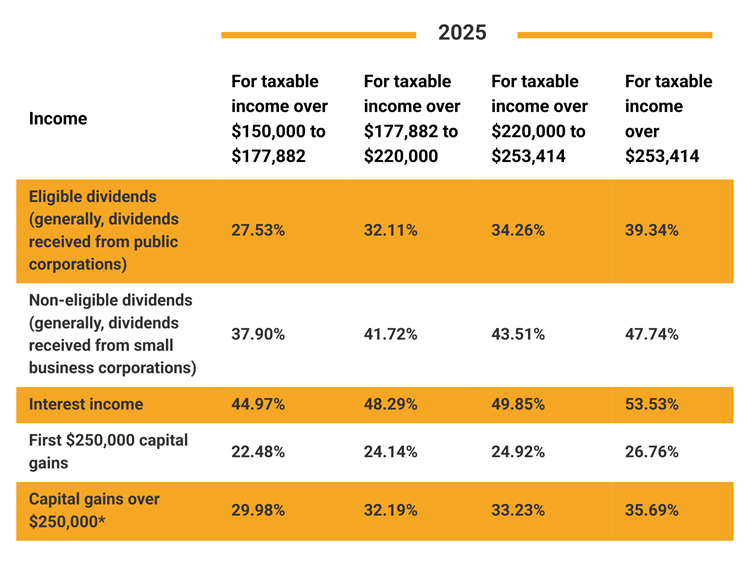
*The tax rate above on capital gains over $250,000 is based on the proposed changes to the capital gain inclusion rate that were announced in 2024. These changes have not been passed into legislation yet, and the process of getting the necessary legislation passed remains uncertain due to ongoing political challenges in the House of Commons.
Consider reevaluating your investment strategy by comparing the pre-tax dividend rates with the pre-tax interest rates using the chart provided in the Investment Income - A Closer Look section at the end of this segment.
2. Defer tax on interest to the following year by investing funds for a one-year term ending in the next calendar year.
3. Defer purchases of mutual funds until early in the next calendar year to minimize taxable income allocated in the current year from the mutual fund.
4. Existing companies that have built up refundable dividend tax on hand (RDTOH) may consider paying dividends to recover this tax. Depending on its year-end, the company may have up to 24 months to enjoy the benefits of the tax refund before the shareholder is required to pay personal tax on the dividend. The individual circumstances should be reviewed, including the marginal tax rate applicable to the recipient shareholder as compared to the dividend refund rate in the corporation (38.33 per cent).
5. Individuals who own qualified small business corporation (QSBC) shares or qualified farm and fishing property may benefit from the lifetime capital gains exemption (LCGE) on the gain realized on the sale of these types of assets. The amount of the LCGE was $1,016,836 in 2024 and is indexed to inflation annually. Budget 2024 has proposed to increase the LCGE to apply to up to $1.25 million of eligible capital gains. The Government has also proposed to raise the exemption for qualified farm and fishing property from $1,000,000 to $1,250,000. The exemption is available on dispositions made on or after April 21, 2015.
6. It is anticipated that the capital gains inclusion rate will increase from 50 per cent to 66.67 per cent effective June 25, 2024. However, individuals will have a limit where the first $250,000 of capital gains incurred in 2025 will still be eligible for the 50 per cent inclusion rate. Consider realizing gains up to $250,000 per annum to capitalize on the lower inclusion rate. Note that these changes have not been passed into legislation yet, and the process of getting the necessary legislation passed remains uncertain due to ongoing political challenges in the House of Commons.
7. Consider realizing accrued losses on investments to shelter capital gains realized this year and/or in the previous three years.
Note that a loss realized capital gains from the disposition of an investment may be denied if you or your spouse or common-law partner repurchase the investment within a short period of time.
8. Should your trading activities be substantial, the handling of your securities may be considered a business for income tax purposes.
If your disposition of securities is considered a business, your profits will be fully taxable as income, and your losses will be fully deductible against any source of income.
To address concerns about your securities disposition being labeled as a business, you can consider filing a one-time, non-revocable election with the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA).
This election will treat all your gains from dispositions of Canadian securities as capital gains, and all your losses as capital losses, for the current year and all future years.
9. Canadian residents 18 years of age and older can contribute to a tax-free savings account. Starting in 2023, the contribution limit is indexed to inflation and rounded to the nearest $500. The annual limit for 2024 and 2025 is $7,000 per annum.
For someone who has never contributed and has been eligible for the TFSA since its introduction in 2009, they will be allowed to contribute up to $102,000 in 2025.
Contributions to a TFSAs are not deductible for income tax purposes. Interest on money borrowed to invest in a TFSA is not tax deductible.
Both contributions to and income earned in a TFSA and withdrawals from a TFSA are tax-free.
There is an option to give money to your spouse for to make a TFSA contribution, however, the income earned on the contributions in your spouse’s TFSA will not be attributed back to you.
You cannot contribute more than your TFSA contribution limit in a given year, even if you make withdrawals from the account during the year. Your contribution room is restored in the year following the withdrawal. If you overcontribute, you may be subject to a penalty tax for each month that you are in an excess contribution position.
10. Starting April 1, 2023, Canadian residents 18 years of age and older who have not owned a home (and who have a spouse that has not owned a home) in the last four years can open an FHSA to assist them with saving to buy their first home in Canada. Individuals can contribute up to $8,000 per year or $40,000 during their lifetime. Contributions are tax deductible and the income earned in the account is tax-free. Withdrawals will be tax-free if they are made to purchase a qualifying home.
For a withdrawal to be tax-free, the individual must be a first-time home buyer, and there must be a written agreement confirming the purchase or construction of a qualifying home before October 1st of the year following the withdrawal. Within one year of purchasing or constructing the home, you must have the intention to establish it as your primary residence. Any remaining funds after making the withdrawal can be transferred to a Registered Retirement Savings Plan (RRSP) or a Registered Retirement Investment Fund (RRIF) with no penalty or reduction in contribution room if the transfer is made by December 31st of the year following the withdrawal. The account must also be closed by December 31st of the year following the withdrawal.
11. Consider donating publicly-traded securities instead of cash.
A tax-advantaged gift of securities can be made to a private foundation as well as to public charities. Generally, an appreciation in the value of the securities will not be subject to capital gains tax if the securities are donated to:
- A registered charity; or
- A private foundation after March 18, 2007. There are special rules that apply to persons not dealing at arm’s length with the foundation. For more information, please contact us.
However, be aware that alternative minimum tax (AMT) may apply to donations of securities (made by you as an individual taxpayer or through a trust) beginning in 2024. While the donation credit (for individuals) or deduction (for corporations) continues to be available for the fair market value of the securities donated, the new AMT landscape may reduce the benefits of donating publicly traded shares, but the impact will depend on your specific financial situation.
To avoid capital gains tax on the appreciated securities, the securities themselves must be transferred to the charity or foundation.
Similar rules will apply to a capital gain on ecologically sensitive land donated to a conservation charity (other than a private foundation).
The donation of flow-through securities may trigger a capital gain to the donor.
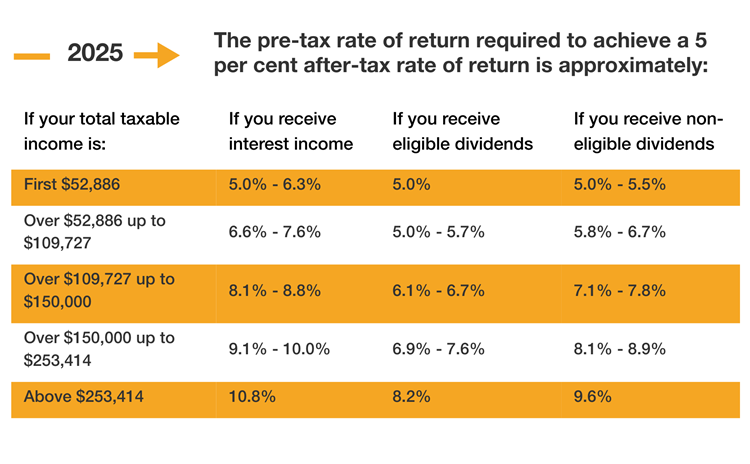
It may be a strategic time for you to consider whether your investment income is tax efficient and consider investment alternatives.
The table below has been prepared to assist you in this matter. It assumes that your investment goal is to earn an after-tax rate of return of five per cent.
It compares the pre-tax yield required to achieve a five per cent after-tax rate of return by earning:
- Interest income;
- Eligible dividends (generally, dividends received from public corporations); or
- Non-eligible dividends (generally, dividends received from small business corporations).
Top 3 Tax Tips for Investors
- Contribute to Tax-Free and First Home Savings Accounts (FHSA): Shift into high gear by leveraging these accounts as powerful investment tools to grow your wealth tax-free.
- Utilize Your Lifetime Capital Gains Exemption (LCGE): Protect your gains and shelter profits where possible to stay ahead on the road to financial success.
- Offset Gains with Losses: Smooth out the bumps by realizing accrued losses to offset capital gains or crystallizing accrued gains up to $250,000 annually to benefit from the lower inclusion rate.
This article has been prepared for the general information of our clients. Please note that this publication should not be considered a substitute for personalized advice related to your situation.
Related Posts
Contact Us







