
Year-end settlement of exact payroll tax and employer’s obligation

During the year, employees are being withheld income taxes and local income taxes on salary and wage income through payroll on a monthly basis based on the Quick Tax Table of the NTS which is updated and announced every year.
In February of the following year after each year-end, employers are required to finalize tax liabilities of its employees (excluding daily workers) by performing year-end tax settlement of exact payroll withholding taxes (“연말정산” in Korean). Any overpayment (or underpayment) of payroll taxes based on the results of year-end settlement should be adjusted in the February payroll as refunds (or additional withholding) and the year-end settlement report should be filed with the tax office by March 10 together with the February payroll.
For year-end settlement of exact payroll withholding taxes, employees are required to gather and submit supporting documents for income deduction and exemption claims in early January of the following year. Based on such income deduction and exemption documents submitted by employees, employers as tax withholding agents shall perform year-end settlement for each individual employee accordingly.
If an employee has salary and wage income only and pays finalized income taxes fully through year-end tax settlement, the employee fulfills his/her income tax reporting obligation and a global income tax return filing by May 31 of the following year will not be needed additionally. On the other hand, if an employee has, in excess of certain limit, other source of income other than salary and wage shall be required to file additionally a global income tax return by May 31 of the following year.
Income tax rates in effect for year 2015 and exemption and deduction claims allowed under the Individual Income Tax Law of Korea can be summarized as below.
- Individual Income Tax Rates
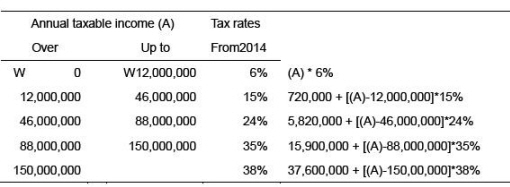
* Local income tax is added at the rate of 10% on income tax liability.
- Exemptions and Deductions from Individual Income
∙ Basic allowance : Won 1,500,000 per person
∙ Earned income deduction:
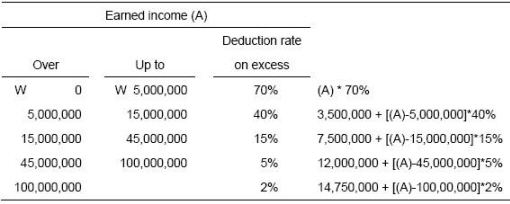
∙ Additional allowances : Varies
Foreigner (non-Korean) employees are eligible for a flat income tax rate of 17% (plus 1.7% local income tax) instead of the progressive income tax rates (an application must be filed with the tax office separately). When choosing the flat income tax rate, however, the expatriates will not be allowed any other benefits including nontaxable income treatment, tax reduction and tax exemption relating to income taxes. As such, if the foreigner employee was applied the 18.7% flat rate during the year, there will be no adjustment required at year-end settlement. In general, for foreigner employee having annual salary and wage income of Won 120 million or more, applying the 18.7% flat tax rate will be more beneficial. For annual income of below Won 120 million, applying progressive tax rate and performing year-end settlement (with eligible income deduction and exemption claims) will be more beneficial.